What is appendicitis? symptoms, Types, Causes
What is appendicitis?
Appendicitis occurs in an internal organ in the body called the appendix. The appendix is a thin and small tube approximately 2 to 3 inches long. It is attached to the intestine where stool is formed in the large intestine. A painful inflammation of the appendix is known as appendicitis.
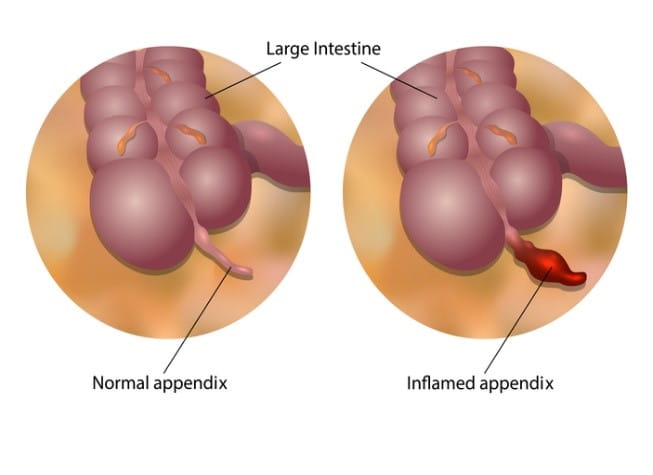
At the beginning of appendicitis, there is usually recurrent pain in the middle part of the abdomen. Within a few hours, the pain starts appearing in the lower right part of the abdomen, where the appendix is located, and the pain becomes severe. Its pain becomes more severe especially when walking, coughing or pressing this area.
Appendicitis causes symptoms like nausea, loss of appetite, fever and red face.
If someone is suffering from appendicitis, then the appendix should be removed from his stomach by surgery as soon as possible. The operation of the appendix is known as appendectomy. If a person is likely to have appendicitis but it is not possible to diagnose it, surgery is recommended. This advice is given because it is better to have the appendix removed rather than risk it rupturing.
The appendix does not perform any important function in the human body and removing it does not cause any long-term problems.
Types of appendix (appendicitis) –
There are two types of appendicitis:
1. Acute appendicitis – Acute appendicitis, like its name, develops very rapidly, usually within a few hours or days. It is easy to detect, and immediate treatment requires surgery. This occurs when the appendix becomes completely blocked due to bacterial infection, stool, or some other type of blockage. When bacteria start multiplying rapidly in the appendix, it causes swelling and formation of pus, which can also cause the appendix to become lifeless.
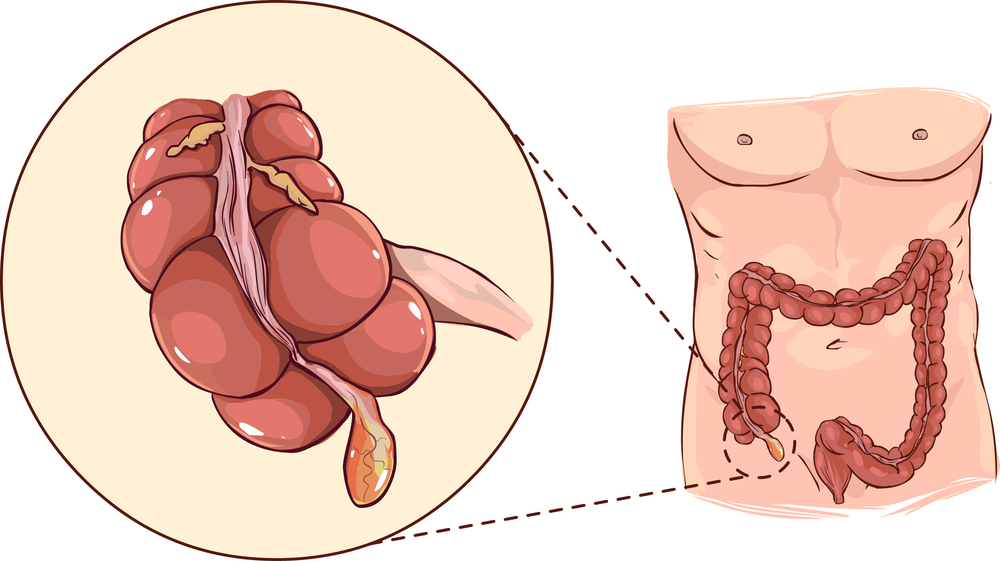
2. Chronic appendicitis – In this the inflammation lasts for a long time. In case of appendicitis, it has been recorded only up to 1.5 percent. With chronic appendicitis, there is a gradual blockage of the appendix which causes inflammation in the tissues around it. The swelling becomes more severe due to internal pressure. However, rather than the appendix bursting, the blockage opens up due to pressure over time. In this way its symptoms can be reduced or even eliminated.
Symptoms of appendix (appendicitis) –
Its early signs and symptoms are often quite mild, including stomach pain and loss of appetite.
And then as appendicitis gradually increases, pain becomes the main symptom, which is not limited to the affected area but starts spreading to the internal organs around it.
Mild pain in the navel or upper part of the abdomen which becomes stronger as it moves towards the lower right part of the abdomen.
Loss of appetite.
Swelling in the stomach.
Fever of 99-102 degrees Fahrenheit.
Mild or severe pain anywhere in the upper or lower abdomen, back, or rectum.
Difficulty urinating.
Severe stomach cramps.
Problem of constipation or diarrhea along with gas.
Appendicitis also affects urination.

Appendicitis is thought to develop when the opening in the appendix, called the cecum, is blocked. This blockage may be caused by a thick mucus-like fluid forming inside the appendix or by stool that passes into the appendix from the cecum. This fluid or feces hardens and becomes as strong as a stone, which gets trapped and closes the hole. This stone-like thing is called ‘fecalith’.
Apart from this, sometimes, the lymphatic tissues of the appendix become swollen and they expand and block the hole. Bacteria are normally found in the appendix, but when there is a blockage, they multiply and begin to attack the layers of the appendix and spread infection.
Prevention of Appendicitis –
There is no other way to prevent appendicitis other than regular health preventive checkups. This is because in this way the internal organs of the body can be examined and their condition can be ascertained.
However, those who consume a diet rich in fiber reduce the chances of having problems like appendicitis. Although its
Treatment of appendix (appendicitis) –
It is generally treated through surgery, with the help of which the appendix is removed from the body. However, some research has shown that treating acute appendicitis with antibiotics may eliminate the need for surgery in some cases.
Generally, if appendicitis is suspected, doctors recommend removing the appendix as soon as possible for the safety of the patient so that the possibility of it bursting can be eliminated.
If an abscess develops in the appendix, there are two ways to get rid of it – one is to drain out the pus or fluid from the abscess and the other is to remove the appendix from the body.
Appendicitis operation (surgery to remove the appendix or appendectomy)
Before surgery, the patient is given antibiotics to prevent infection.
There are two options for surgery on the appendix (also known as appendectomy). First, it can be performed as an open surgery, in which an incision is made in the abdomen that ranges from two to four inches in length. Another option is laparoscopic surgery. This surgery is performed by making a few small incisions in the abdomen. During laparoscopic surgery, many special surgical instruments are required, including a small video camera.